Imitation Learning: A Powerful Approach to Learn Optimal Policies
- Tech news
- July 26, 2023
- No Comment
- 26
Imitation Learning: A Brief Overview
Imitation Learning (IL) is an area of machine learning that addresses the challenge of learning optimal policies in environments with sparse rewards or when direct reward functions are difficult to specify. In IL, an expert provides a set of demonstrations to guide the learning process, and the agent imitates the expert’s decisions to learn the optimal policy. This approach proves useful in situations where it is easier for an expert to demonstrate desired behavior than to define a reward function or directly learn the policy.
Basics of Imitation Learning
In IL, the environment is typically modeled as a Markov Decision Process (MDP), with states, actions, and transition probabilities. The agent interacts with the environment based on its policy, aiming to maximize the cumulative rewards over time. Demonstrations from the expert provide examples of state-action pairs that guide the learning process.
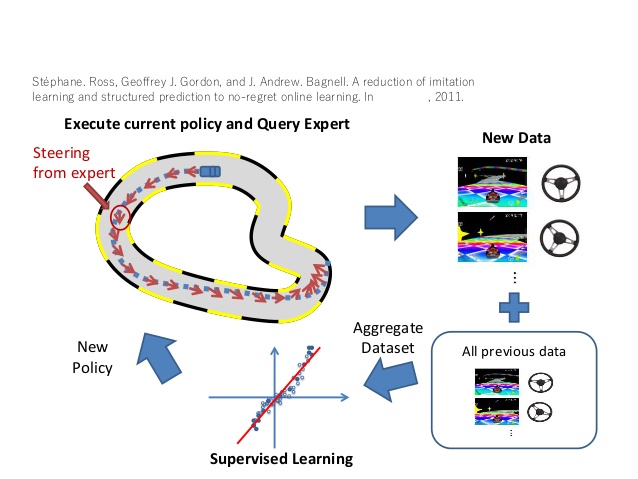
Behavioural Cloning
Behavioural Cloning (BC) is a simple form of IL that uses supervised learning to learn the expert’s policy from demonstrations. The demonstrations are divided into state-action pairs, treated as independent examples, and used to train the agent’s policy. While BC can work well in some cases, it may fail in environments with non-i.i.d. data, where errors in different states can compound, leading to unforeseen failures.
Direct Policy Learning (via Interactive Demonstrator)
Direct Policy Learning (DPL) is an improved version of BC that addresses some of its limitations. DPL assumes access to an interactive demonstrator during training, allowing the agent to query the expert for evaluations and more demonstrations. The iterative process involves updating the policy based on the feedback from the expert and repeating until convergence.
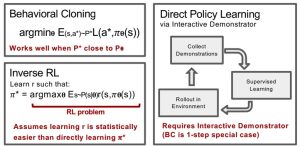
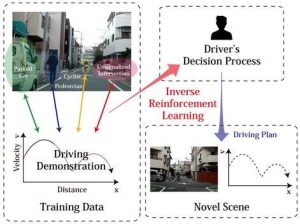
Inverse Reinforcement Learning
Inverse Reinforcement Learning (IRL) is another approach to IL that focuses on learning the reward function from expert demonstrations. Once the reward function is estimated, reinforcement learning is used to find the optimal policy that maximizes this reward function. IRL can be model-given or model-free, depending on whether we know the environment’s state transition dynamics and the complexity of the reward function.
The Maximum Entropy Principle
In IRL, learning the reward function can be ambiguous, as multiple reward functions can lead to the same optimal policy. The maximum entropy principle is used to select the trajectory distribution with the highest entropy to address this issue.
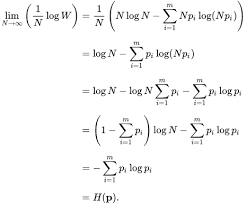
Imitation Learning offers an alternative approach to reinforcement learning when rewards are sparse or hard to define. By leveraging expert demonstrations, IL provides a means to learn optimal policies and find applications in various fields, such as autonomous vehicles and robotics.









