Essential Networking Command Line Tools for Troubleshooting
- Tech news
- July 31, 2023
- No Comment
- 32
Introduction to Networking Command Line Tools
Networking command line tools play a crucial role in the daily activities of IT personnel, especially when troubleshooting network issues. These tools offer valuable insights into the network’s configuration and performance, helping identify and resolve problems efficiently. In this article, we will explore some essential command line tools that come in handy for troubleshooting networking environments.
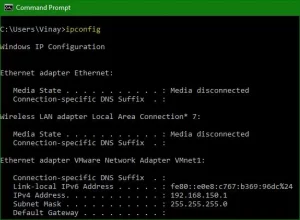
IPCONFIG and IFCONFIG: Viewing TCP/IP Configuration
The IPCONFIG command is a valuable tool in the Windows operating system, providing basic information about the TCP/IP configuration. It reveals essential details such as the IP address, router’s IP address, DNS server IP address, and DHCP server IP address. Similarly, the ‘ifconfig’ command serves the same purpose in Unix, Linux, and Macintosh operating systems.
PING: Checking Connectivity between Devices
One of the most powerful and straightforward networking command line tools is PING. It is used to check connectivity between networking devices. By employing the ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol), the ping command sends out an “echo request” to the destination device. If the device is active and reachable, it responds with an “echo response.” PING is an invaluable tool for network administrators to verify network connectivity quickly.
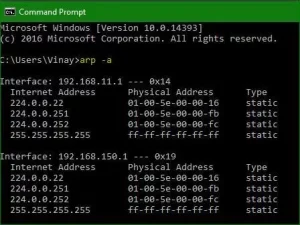
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP): Resolving IP and MAC Addresses
The ARP is both a protocol and a utility that resolves IP addresses to MAC addresses and vice versa. It acts as a resolution protocol, crucial for establishing communication between devices. Network devices maintain an ARP cache in memory, containing the mappings of IP addresses to MAC addresses. This cache helps in reducing network traffic by resolving addresses efficiently.
TRACERT: Tracing Packet Paths in Windows
The tracert command is a valuable tool in the Windows operating system, allowing users to view the complete path a packet takes to reach its destination device. As a packet travels from the source to the destination, it goes through various routers or “hops” in the network. Tracert displays the list of routers (or hops) a packet encounters along its journey, providing valuable insights into the network’s routing path.
NSLOOKUP and DIG: Troubleshooting DNS Name Resolution
NSLOOKUP is a command used in the Windows operating system to troubleshoot DNS name resolution issues. It operates in interactive and non-interactive modes, allowing users to query DNS servers and obtain information about domain names, IP addresses, and other DNS-related details. In Unix, Linux, and Macintosh operating systems, the DIG command serves the same purpose as NSLOOKUP but lacks an interactive mode. DIG is considered more powerful due to its advanced features and capabilities.
NETSTAT: Analyzing TCP/IP Network Statistics and Connections NETSTAT is a valuable command-line tool used to display TCP/IP network statistics and active connections on a system. It provides information about active connections, open ports, and network statistics, making it a useful tool for troubleshooting network issues. By analyzing network statistics, administrators can identify potential problems and take appropriate actions to optimize network performance.
Conclusion
Networking command line tools are indispensable resources for IT personnel when it comes to troubleshooting network-related problems. From examining TCP/IP configurations to diagnosing DNS name resolution issues and analyzing network statistics, these tools provide crucial insights into network performance and connectivity. By mastering these command line tools, network administrators can efficiently resolve issues and maintain a stable and reliable network infrastructure.









